Page 29 - Respond 2020 Magazine
P. 29
RESPOND
EUROPE WILL SUPPORT EUROPEAN SPACE AGENCY (ESA)
CLIMATE ACTION FROM SPACE The European Space Agency (ESA) is an
intergovernmental organisation with the mission to
shape the development of Europe’s space capability
and ensure that investment in space delivers
benefits to the citizens of Europe and the world.
new satellite constellation is set to provide Once in orbit, the mission’s satellites will carry several ESA develops the launchers, spacecraft and ground
global carbon dioxide emission monitoring spectrometers measuring in the visible, and near- and facilities needed to keep Europe at the forefront of
A and support progress towards the Paris shortwave-infrared spectral ranges, and additionally global space activities. ESA is working in particular
Agreement goals. sensors for measuring clouds and aerosol, which will allow
for retrieving accurate images of anthropogenic CO2. The with the EU on implementing the Galileo and
A new satellite mission due to launch in 2025 will feed the capability of distinguishing between naturally-occurring Copernicus programmes as well as with EUMETSAT
first global system for tracking carbon dioxide emissions emissions and those generated by burning fossil fuels will for the development of meteorological missions.
from fossil fuel combustion. It will equip countries with the support the intense emissions-reduction efforts of the future.
information they need to decarbonise their economies in
According to ESA’s CO2M mission scientist Dr Yasjka Meijer,
order to meet their Paris Agreement commitments.
who is involved in detailing the new satellite’s specifications,
Planning for the new Copernicus anthropogenic CO2 the mission will deliver data at a scale and accuracy that allow as judge the impact of policy measures to reduce our in advancing the scientific understanding of climate. Through
monitoring mission - dubbed CO2M - is at an advanced carbon dioxide emissions to be traced from continental, to dependence on fossil fuels, such as switching energy the ESA Climate Change Initiative, long-term and unified
stage. It is being developed jointly by ESA, the European country, to sub-national scales, “and will even identify sources sources or implementing congestion charging. records of Essential Climate Variables provide a whole-globe
Commission, EUMETSAT and ECMWF, with funds subject from cities or even single sources such as power stations.” view of the climate. These time series of climate variables
to budgetary approval. The mission is intended to support, The satellite’s capability of also measuring the co-emitted Dr Meijer adds, “the data are independent and will act as such as sea-level rise, melting glaciers and changing
among others, the global stocktake, a mechanism under NO2 supports the discrimination of individual plumes. a useful cross-check, adding greater confidence with polar ice sheets have supported the IPCC in its summary
Article 14 of the Paris Agreement for assessing each measurements in national emissions inventories.”
He adds that, “existing satellites give a relatively sparse view statements, including the recent special report on oceans
country’s progress towards cutting emissions and reviewing and cryosphere.
of global CO2 and so don’t usefully inform the impact of Being publicly available, there will also be an added layer
targets that will need to be assessed every five years.
emissions reduction policies at a national level.” of transparency and accountability that is anticipated to This new mission builds on this understanding and will play
Accurate and detailed information on concentrations and encourage best practice.
By contrast, CO2M will provide a global view with sufficient a crucial role in enabling the international community to take
emissions of greenhouse gases is becoming increasingly the steps necessary to avert major climate disruption.
accuracy to capture plumes from individual sources. Its Data from CO2M is expected to be collected on an
urgent. Global average temperatures have already warmed
satellites, with a swath of 250 kilometres, will be able to operational basis from 2026 onwards, in time to inform the
by around 1C since pre-industrial times. The Arctic Carbon dioxide is on the rise. The planned ESA
provide 250 data points per second. This enables the 2028 global stocktake.
is undergoing a faster transition to a warmer climate, CO2M mission will help track progress towards Paris
constellation to scan the entire planet every two to three days.
with annual warming two to three times higher than the Satellite observations collected by ESA and its Member Agreement goals.
global average. Levels of atmospheric CO2 – which after This improved capability is set to both enable countries States over the past four decades have played a pivotal role
www.esa.int
atmospheric water vapour makes the biggest contribution to to assess progress towards their 2030 national emissions
the greenhouse gas effect – reached a record 418 parts per reduction targets as part of the Paris Agreement, as well
million (ppm) in 2018 and is anticipated to continue to rise.
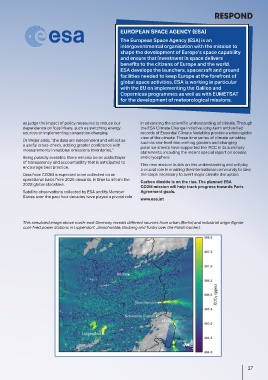
The new CO2M of the European Copernicus programme will monitor man-made carbon dioxide from space and reveal its This simulated image above north-east Germany reveals different sources from urban (Berlin) and industrial origin (lignite
emission sources. coal-fired power stations in Lippendorf, Jänschwalde, Boxberg and Turów over the Polish border).
26 27